Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Dental Imaging
Thanks to the sophisticated capabilities it offers practitioners for diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient education, digital dental imaging has completely transformed the dental sector. Considering all of its benefits, digital imaging technologies have essentially supplanted traditional film-based radiography.
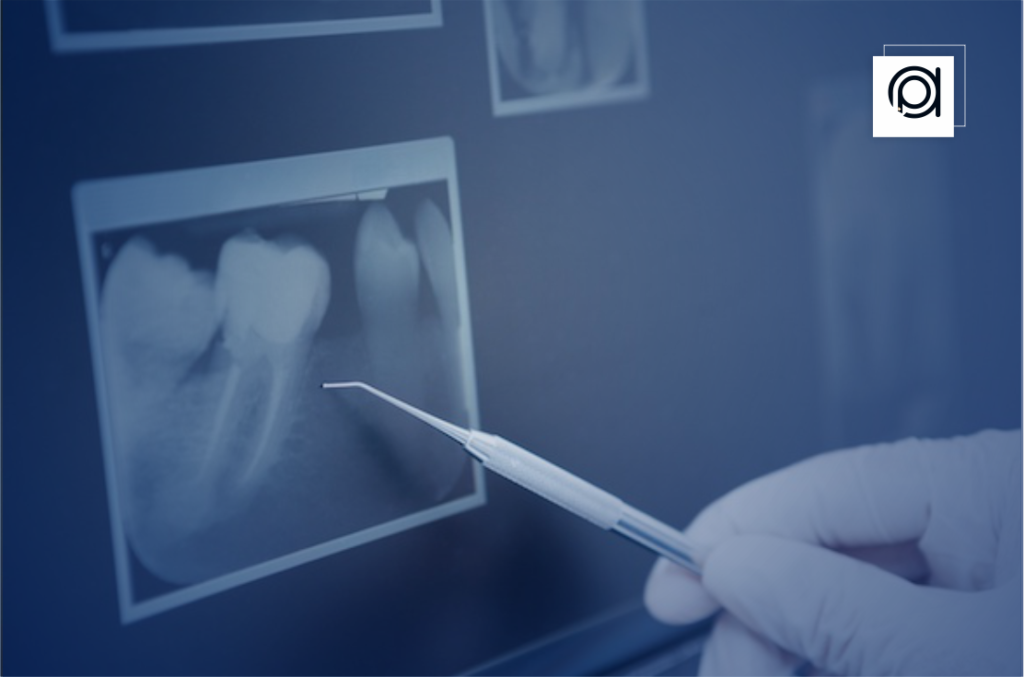
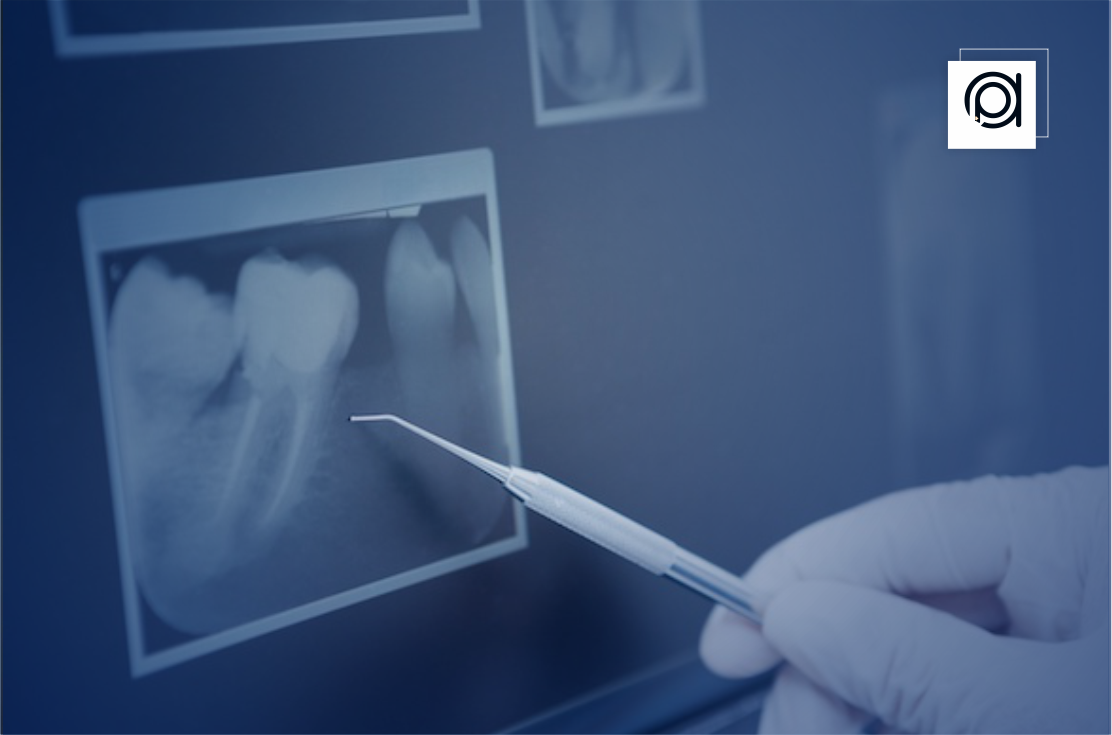
In contrast to conventional film-based radiography, which uses electronic sensors to record images that are subsequently shown digitally on a computer screen, digital dental imaging uses electronic sensors to record images on X-ray film that need to be developed chemically.
What is Digital Dental Imaging?
Digital Dental Imaging is the process of taking, storing, and modifying pictures of teeth, gums, and surrounding tissues for use in diagnosis and treatment planning in dentistry. By giving dentists access to cutting-edge instruments for precise diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient care, digital dental imaging has completely transformed the dental industry.
Digital dental imaging does, however, have a few disadvantages, just like any other technology. This article aims to clarify the benefits and drawbacks of digital dental imaging while also examining how technology has affected contemporary dental procedures.
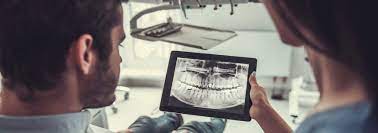
Advantages of Digital Dental Imaging
In order to take, store, and process pictures of the teeth, jaws, and surrounding oral structures for diagnostic and therapeutic reasons in dentistry, a process known as digital dental imaging is used.
Due to its many benefits, which include better image quality, lower radiation exposure, and increased workflow efficiency, this technology has essentially supplanted traditional film-based radiography.
Improved Image Quality
Digital dental imaging produces high-resolution images, allowing dentists to detect even the minutest details such as cavities, fractures, and bone loss with greater clarity compared to conventional film radiography.
Reduced Radiation Exposure
Digital imaging systems require significantly less radiation exposure compared to traditional X-ray films, ensuring the safety of both patients and dental professionals. This reduction in radiation is particularly beneficial for pediatric patients and individuals undergoing frequent imaging.
Instant Image Acquisition:
Unlike traditional film radiography that requires chemical processing, digital dental imaging provides instant results. Dentists can view images immediately on a computer screen, facilitating quick diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Enhanced Storage and Retrieval
Digital images can be stored electronically, eliminating the need for physical storage space and minimizing the risk of damage or loss. Additionally, these images can be easily retrieved and shared with other healthcare providers, improving collaboration and continuity of care.
Environmentally Friendly
Digital dental imaging eliminates the use of chemicals and film processing, reducing the environmental impact associated with traditional radiography. This aligns with the growing trend of eco-conscious practices in healthcare.
Patient Education
Digital images can be displayed on chairside monitors, allowing dentists to visually explain dental conditions and treatment options to patients in real-time. This enhances patient understanding and facilitates informed decision-making.

Disadvantages of Digital Dental Imaging
Notwithstanding these benefits, there are many drawbacks to digital dental imaging as well, such as the requirement for continuous maintenance and training, high equipment startup costs, and technological complexity. Digital technology is an essential tool for contemporary dental clinics, nonetheless, since its advantages exceed these drawbacks.
Initial Cost
The upfront cost of implementing digital imaging systems can be substantial for dental practices, including the purchase of digital sensors, software, and training for staff. This initial investment may pose a barrier for smaller practices or those with limited financial resources.
Technical Complexity
Digital imaging systems require specialized equipment and software, necessitating training for dental professionals to operate them effectively. Technical issues such as sensor malfunction or software glitches may also arise, leading to downtime and potential disruptions in patient care.
Image Distortion
Despite advancements in technology, digital dental images may still exhibit distortion or artifacts, particularly in areas of anatomical complexity such as roots or overlapping structures. This can affect the accuracy of diagnosis and treatment planning.
Workflow Integration Challenges
Transitioning from traditional film radiography to digital imaging may disrupt existing workflow patterns within dental practices. Integration with electronic health records (EHR) systems and adaptation to new digital workflows may require time and adjustment.
Limited Accessibility
In some regions, especially rural areas or developing countries, access to digital dental imaging technology may be limited due to infrastructure constraints or financial barriers. This disparity in access can widen existing healthcare disparities and hinder the delivery of quality dental care.
Data Security Concerns
Digital dental images contain sensitive patient information and must be protected against unauthorized access or cyber threats. Dental practices must invest in robust data security measures to safeguard patient privacy and comply with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA.
The Crucial Role of Liability Insurance for Health Professionals
Conclusion
Many benefits come with digital dental imaging, including as better patient education, lower radiation exposure, and higher-quality images. But there are drawbacks as well, such upfront costs, complicated technological requirements, and problems with process integration.
Notwithstanding these limitations, the global deployment of digital imaging equipment has revolutionized dentistry practices by facilitating more effective patient care, diagnosis, and treatment planning. In order to fully utilize digital dental imaging and advance dentistry, it will be imperative to solve its limits as technology develops.